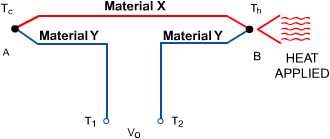
Introduction to thermoelectric effect
TEC, TEA, semiconductor refrigeration sheet, semiconductor module, refrigeration sheet